

Occasionally letters or diacritics are added, removed, or modified by the International Phonetic Association. Often, slashes are used to signal broad or phonemic transcription thus, /t/ is less specific than, and could refer to, either or depending on the context and language. For example, the sound of the English letter ⟨t⟩ may be transcribed in IPA with a single letter,, or with a letter plus diacritics,, depending on how precise one wishes to be. IPA symbols are composed of one or more elements of two basic types, letters and diacritics. To represent additional qualities of speech such as tooth gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft palate, an extended set of symbols called the Extensions to the IPA may be used. The IPA is designed to represent only those qualities of speech that are distinctive in spoken language: phonemes, intonation, and the separation of words and syllables. The IPA is used by foreign language students and teachers, linguists, Speech-Language Pathologists, singers, actors, lexicographers, constructed language creators ( conlangers), and translators.
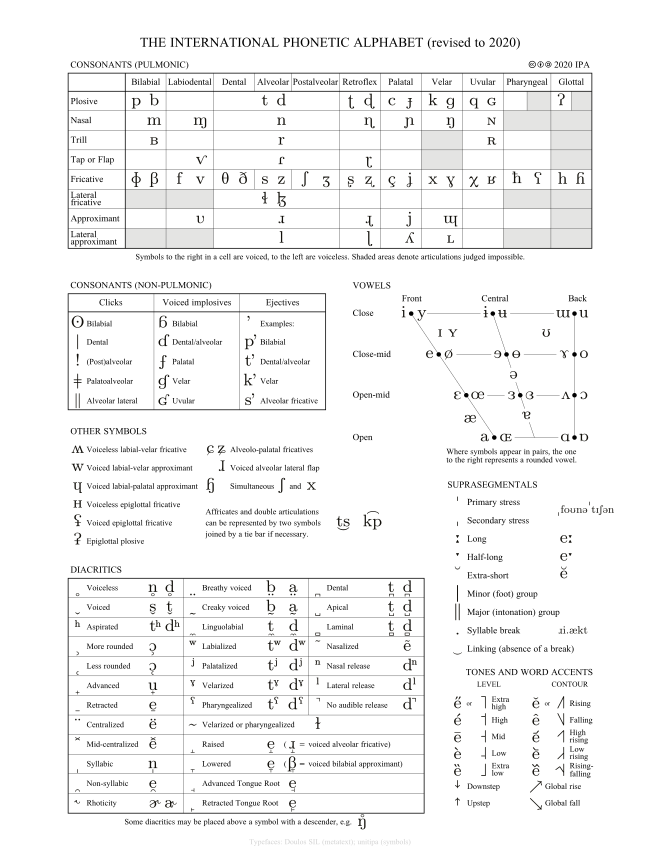
It was devised by the International Phonetic Association as a standardized representation of the sounds of spoken language. The International Phonetic Alphabet ( IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin alphabet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
